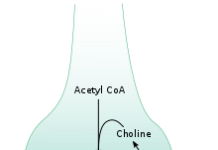
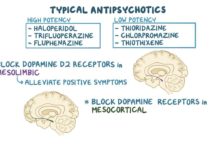
Antidepressants are a drug class that balance certain chemicals in the brain that affect mood and behavior.
Antidepressants are a drug class that moderate certain chemicals in the brain that affect mood and behavior.
These medicines were first developed in the 1950s. Today, experts estimate that about 10 percent of Americans takes an antidepressant.
The medicines are used to treat a variety of conditions, including:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Agitation
- Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Social anxiety disorder
- Manic-depressive disorder
- Major depressive disorder
- Post-traumatic stress syndrome (PTSD)
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Eating disorders
- Bedwetting
- Neuropathy pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Hot flashes
- Premenstrual symptoms
- Chronic hives
It can take several weeks for antidepressants to begin to work. They are typically taken for months or years at a time.
There are several different classes of antidepressants. These include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs)
- Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NaSSAs)
Common Antidepressants
There are many antidepressants on the market. Some of these include:
- Citalopram (Celexa)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro)
- Fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem)
- Fluvoxamine (Luvox)
- Paroxetine (Paxil)
- Sertraline (Zoloft)
- Amitriptyline (Elavil)
- Imipramine (Tofranil)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Protriptyline (Vivactil)
- Trimipramine (Surmontil)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Phenelzine (Nardil)
- Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
- Isocarboxazid (Marplan)
- Trazodone Bupropion (Wellbutrin)
Antidepressant Side Effects
Antidepressants can cause side effects, including:
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Insomnia
- Increased appetite
- Constipation
- Agitation or irritability
- Anxiety
- Loss of sexual desire or other sexual problems
- Erectile dysfunction
Antidepressants are required to carry a black-box warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
In short-term studies, the medicines increased the risk of suicidal tendencies in some children and young adults with depression or psychiatric disorders.
These effects were most pronounced in the weeks after starting on a course of antidepressants, or when increasing the dosage.
A 2016 analysis published in the journal BMJ found that the use of antidepressants can double the risk of aggressive behavior and suicide in children.
Additionally, you may experience unpleasant withdrawal symptoms if you stop taking an antidepressant suddenly.
Talk to your doctor about these potential effects and how to minimize withdrawal symptoms or avoid them entirely.
Antidepressants and Weight Gain
Weight gain is another common side effect of antidepressants.
Some studies show up to 25 percent of people who take these medicines gain a significant amount of weight.
You can minimize this unwanted effect by exercising and following a healthy eating plan.
Since some antidepressants are more likely to lead to weight gain than others, talk to your doctor about switching to another medication if the antidepressant you are taking seems to be causing your weight problems.
Antidepressants and Pregnancy
Taking an antidepressant during pregnancy may cause risks for an unborn baby, but for some pregnant women not treating depression poses risks, too.
Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of taking antidepressants during pregnancy.
Some antidepressants do enter breast milk but there is no conclusive evidence that this is harmful to a breastfeeding infant.
Nevertheless, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of taking an antidepressant if you are breastfeeding.
Antidepressants and Alcohol
Drinking alcohol while taking an antidepressant can worsen your symptoms and increase your risk of certain side effects.
Talk to your doctor about the potential interaction between alcohol and antidepressants.


Editorial Sources and Fact-Checking
- What are Antidepressants? Medical News Today.
- Why is it Bad to Mix Alcohol and Antidepressants? Mayo Clinic.
- A Glut of Antidepressants, The New York Times.