Ultrasound is best known for providing images of developing fetuses, but they’re also used for several types of therapies.
An ultrasound is a non-invasive medical technique that makes use of high-frequency sound waves.
It’s best known for its use during pregnancy as the primary method to visualize fetuses developing in the womb.
Medical ultrasound falls into two broad categories: diagnostic and therapeutic.
Diagnostic Ultrasound
Diagnostic ultrasound, also known as sonography or ultrasonography, use sound to image organs and structures inside of the body, helping to diagnose medical issues.
Images produced by diagnostic ultrasound are called sonograms.
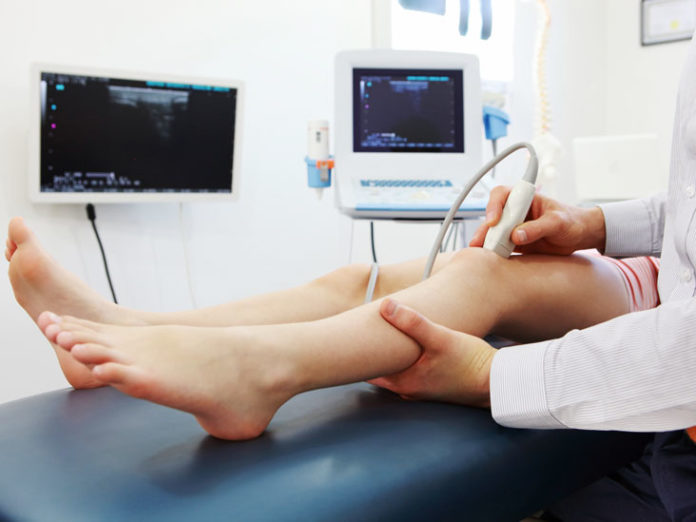
During a diagnostic ultrasound, you are positioned on a medical table so the part of your body being imaged is accessible.
Your doctor or a technician will apply a water-based gel, which helps transmit sound waves, to your skin over the area that needs to be visualized.
Your doctor will then guide a handheld device, called a transducer, over the gelled skin.
The transducer sends into the body a directed beam of sound waves with frequencies above human hearing (above 20 KHz), which reflect back off of tissues and organs.
The transducer analyzes these echoes and converts them into sonograms that are displayed on a monitor.
Diagnostic ultrasound can also be performed internally. For instance, to view the prostate, a transducer is attached to a probe and inserted into a man's rectum.
A transvaginal ultrasound uses a transduce inserted in the vagina to better view a woman’s reproductive organs and urinary tract.
Diagnostic ultrasound can image a wide range of internal structures, including the heart and blood vessels, liver, and thyroid, among others.
It can be used to:
- Evaluate and identify the source of pain, swelling, and infections
- Diagnose heart conditions
- Detect tumors
- Evaluate issues that affect blood flow, such as narrowed blood vessels and clots
- Guide invasive procedures, including needle biopsies and needle-based anesthesiology
- Detect brain abnormalities in newborns
Therapeutic Ultrasound
Therapeutic ultrasound use very high-frequency sound waves to modify or destroy tissue.
The procedures vary, depending on your therapeutic needs. Uses for therapeutic ultrasound include:
- Breaking up large kidney stones and gallstones
- Ablation (removal) of uterine fibroids, or noncancerous growths in the uterus
- Teeth cleaning
- Cataract removal
- Physical therapy (warming of tendons, muscles, and other tissues) for conditions such as tendonitis
- Treatment of tumors and cysts
- Stimulating bone growth to heal fractures
- Surgical tissue cutting and hemostasis (stopping of blood flow)
Ultrasound has also been used to help guide the delivery of drugs to specific tissues.