Ear pain can arise gradually or all of a sudden. The pain can feel dull, sharp, or burning, and can be temporary or ongoing. Usually, the pain arises in only one ear, but sometimes it can appear in both ears.
Signs and Symptoms of Ear Pain
Symptoms that can accompany ear pain include:
- Fever
- Drainage from the ear
- Hearing loss
- Headache
- Difficulty chewing
- Jaw pain
- Clicking or popping
- Fussiness and irritability (in children)
- Increased crying (in children)
- Loss of appetite (in children)
Causes and Risk Factors of Ear Pain
- Allergies
- Sinus infection
- Sore throat
- Tooth infection
- Buildup of earwax
- Ruptured eardrum
- Altitude pressure changes (barotrauma)
- Temporomandibular joint syndrome (TMJ, or problems with the joint that connects your jaw to the side of your head)
- Arthritis of the jaw
How Is Ear Pain Diagnosed?
Prognosis of Ear Pain
Treatment and Medication Options for Ear Pain
The treatment for ear pain often depends on what’s causing the problem. Common treatments include medication, surgery, and home remedies.
Medication Options
A buildup of earwax in the ear canal can cause an earache. Still, never stick anything into your ear — including a cotton swab, which will just push the wax deeper into the ear instead of removing it. Excessive earwax should be diagnosed and treated by a healthcare professional.
Home Remedies and Alternative and Complementary Therapies
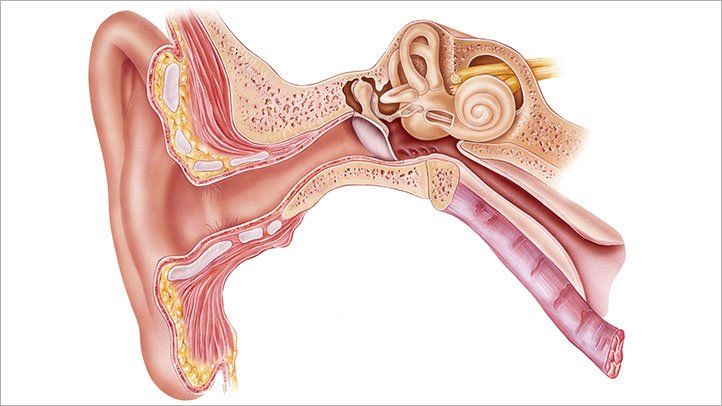

What Are the Possible Complications of Ear Infections?
Surgery Options
Prevention of Ear Pain
Ear pain isn’t always preventable, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk of ear injuries and ear infections.
Research and Statistics: Who Has Ear Pain?
Resources We Love
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
The NIDCD is a research institution and part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Since its founding in 1988, its funding and support has led to discoveries that have helped millions of people with hearing, speech, and language disorders.
ENT Health
This website, run by the American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, offers information on a number of conditions affecting the ears; it also explains what ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialists do and why you may need to see one about ear pain you're experiencing.
Editorial Sources and Fact-Checking
- Ear Pain: Diagnosing Common and Uncommon Causes. American Academy of Family Physicians. January 1, 2018.
- Ear Infections. MedlinePlus. November 6, 2020.
- Ear Infections in Children. National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. May 12, 2017.
- Swimming and Ear Infections. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. June 3, 2020.
- Swimmer's Ear. Mayo Clinic. June 28, 2019.
- Earache. MedlinePlus. January 1, 2020.
- Ear Infection. Cleveland Clinic. April 16, 2020.
- Ear Infection (Middle Ear). Mayo Clinic. May 14, 2019.
- Ruptured Eardrum. MedlinePlus. November 23, 2020.
- Ear Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. August 27, 2019.
- Ears and Altitude. ENT Health. August 2018.
- Marom T, Marchisio P, et al. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Treatment Options for Otitis Media. Medicine. February 2016.
- TMJ Disorders. MedlinePlus. November 23, 2020.
- Swimmer's Ear. MedlinePlus. August 5, 2018.
- Ear Tubes. ENT Health.